Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) is gaining attention as a natural way to support fertility in both men and women. This deep dive explores what CoQ10 is, how it works in the body, why it matters for egg and sperm health, and how you might use it to boost your fertility journey.
Table of contents
- Key takeaways:
- What is coenzyme Q10?
- How does coenzyme Q10 work in the body?
- Coenzyme Q10, the body’s power station fuel
- The hydroelectric dam inside our cells
- CoQ10, the fire brigade inside you
- In summary:
- Why does coenzyme Q10 matter for fertility?
- Coenzyme Q10 and female fertility
- Coenzyme Q10 and male fertility
- What forms of coenzyme Q10 are available?
- How much coenzyme Q10 should I take for fertility?
- How long should I take coenzyme Q10 for fertility?
- Practical tips for boosting fertility with coenzyme Q10
- FAQs
- What is coenzyme Q10, and why is it important for fertility?
- Does coenzyme Q10 improve egg quality?
- Can coenzyme Q10 help male fertility?
- How much coenzyme Q10 should I take for fertility?
- Is it better to take ubiquinone or ubiquinol?
- How long should I take coenzyme Q10 before trying to conceive?
- Can I get enough coenzyme Q10 from food?
- Are there any side effects of coenzyme Q10?
- Can I take coenzyme Q10 with other fertility supplements?
- Where can I buy coenzyme Q10?
- References
Key takeaways:
- Coenzyme Q10 plays a central role in cellular energy and acts as a powerful antioxidant, supporting both male and female fertility [1].
- CoQ10 levels naturally decline with age, which can impact egg and sperm quality [2].
- Supplementing with CoQ10 may improve ovarian reserve, embryo quality, and sperm parameters [6],[7].
- CoQ10 comes in two main forms (ubiquinone and ubiquinol) and can be taken as capsules or an oral patch—absorption matters!
- Most fertility experts recommend taking CoQ10 for at least three months to support egg or sperm health [2].

What is coenzyme Q10?
Coenzyme Q10, often called CoQ10, is a vitamin-like compound found in every cell of your body. Its main job is to help your cells turn food into energy.
Think of it as a microscopic courier, shuttling electrons around the mitochondria (your cells’ power stations) to keep everything running smoothly [1].
But CoQ10 isn’t just about energy. It’s also a powerful antioxidant, helping to mop up harmful free radicals that can damage cells—including eggs and sperm [3].
How does coenzyme Q10 work in the body?
CoQ10’s main claim to fame is its role in the electron transport chain—a fancy phrase for the process that makes ATP, the energy currency of your body [4]. Without enough CoQ10, your cells struggle to make energy efficiently. This is especially important for eggs and sperm, which need a lot of energy to mature, fertilise, and develop properly.
Coenzyme Q10, the body’s power station fuel
CoQ10 is a natural substance found in every cell of your body. Think of it as a tiny helper that keeps your body’s “power stations” (called mitochondria) running smoothly. These power stations don’t make electricity—they make a type of energy called ATP, which your cells need to do everything from moving muscles to growing hair.
The hydroelectric dam inside our cells
Imagine your mitochondria are like big hydroelectric dams. Water (in this case, tiny particles called protons) flows through turbines to make energy. CoQ10’s job is like a bucket brigade, carrying important parts (electrons) from one spot to another inside the dam. If there aren’t enough buckets (CoQ10), the whole process slows down, and you get less energy.
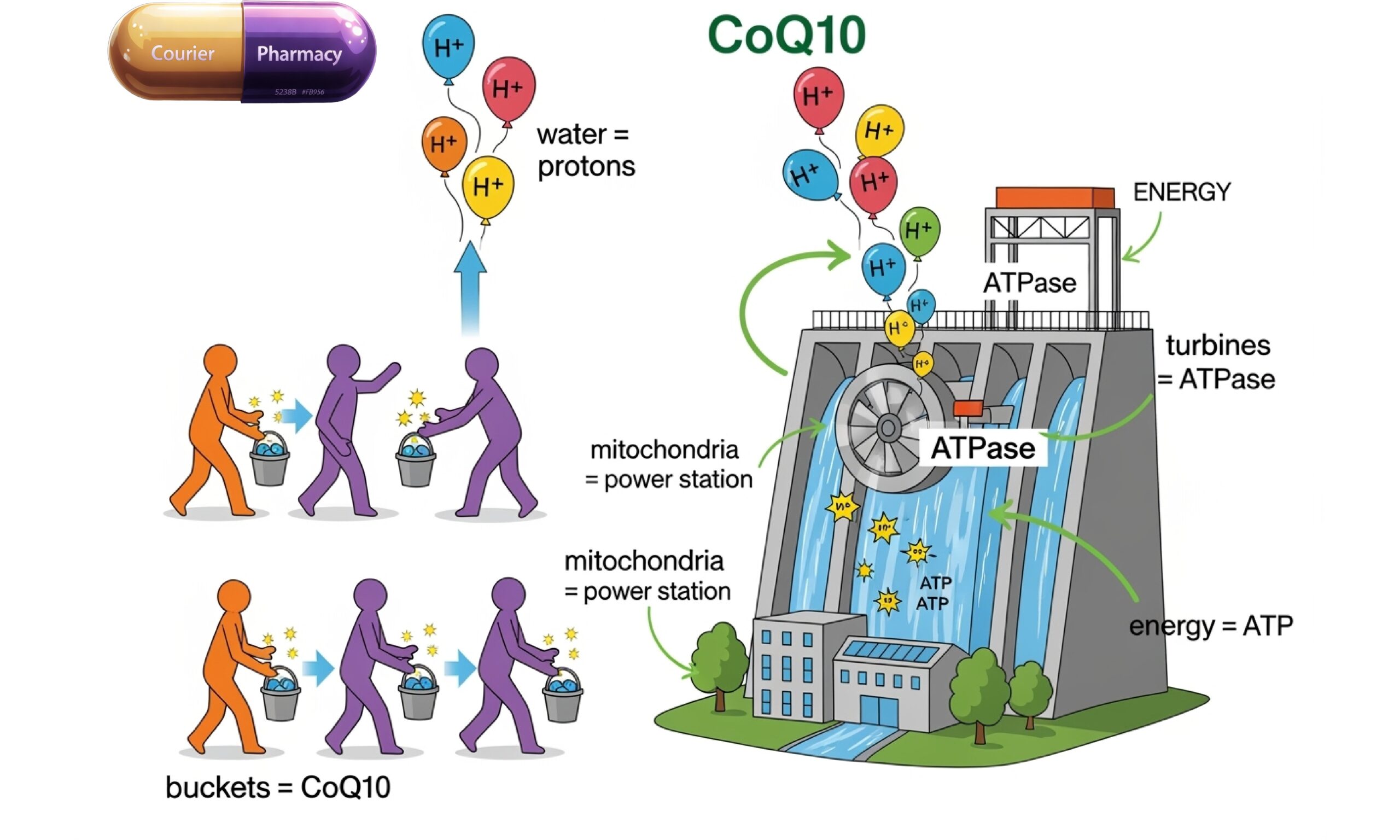
CoQ10, the fire brigade inside you
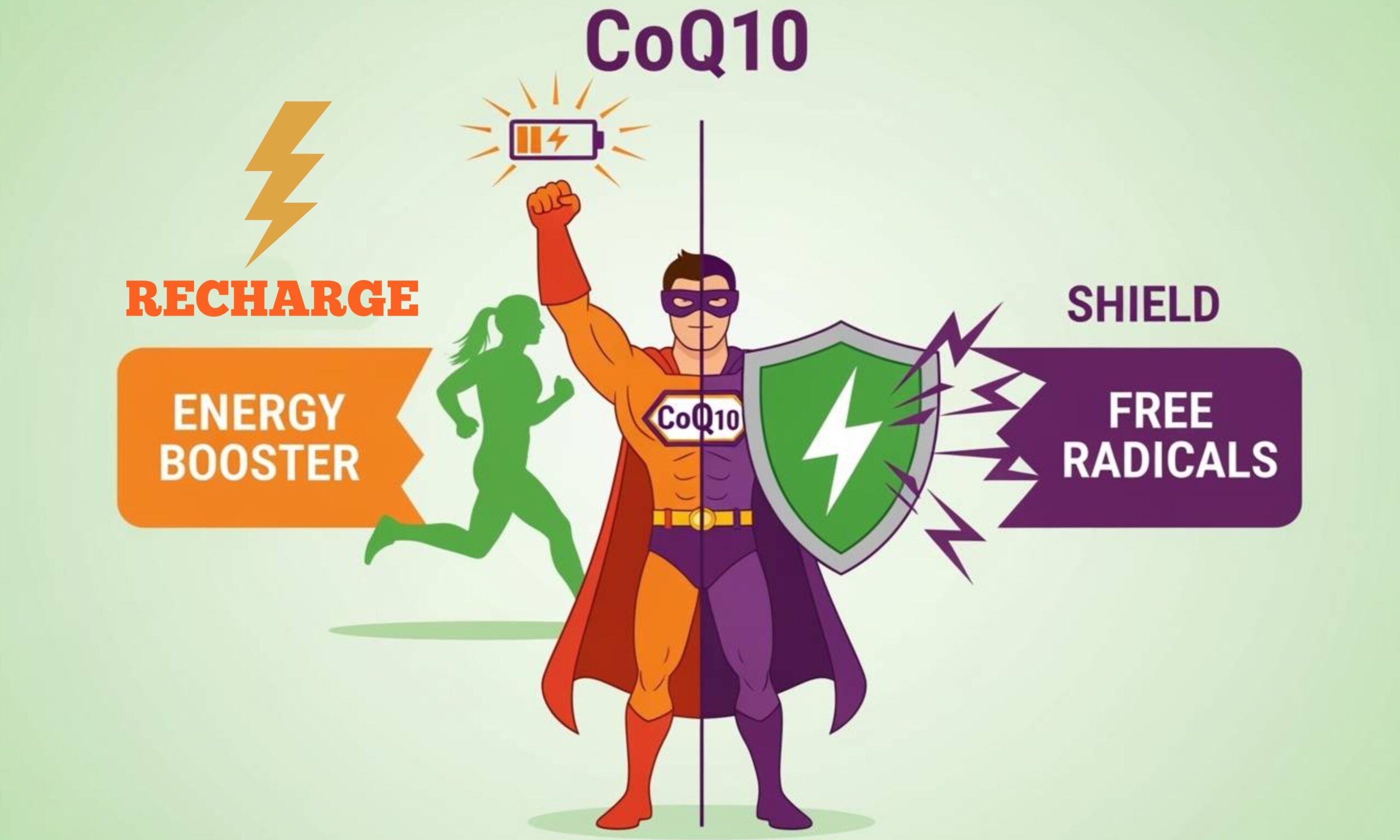
On top of that, CoQ10 acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from the havoc caused by free radicals. It’s like tiny fire engines putting out the fires caused by the marauding free radicals.
This dual action—energy production and antioxidant defence—makes CoQ10 a superstar for reproductive health [3].

In summary:
CoQ10 helps your body turn food into energy and keeps your cells healthy by acting as both an energy booster and a shield against damage.
Why does coenzyme Q10 matter for fertility?
We’re at our most fertile in our teens and early twenties, but as we age, our natural CoQ10 levels start to drop. Lower CoQ10 means less energy for our cells, including eggs and sperm. For women, this can mean poorer egg quality and a higher risk of miscarriage or chromosomal issues. For men, it can lead to lower sperm count, motility, and quality [2].
If your body can’t make enough CoQ10, fertilisation and embryo development can be affected, raising the risk of infertility or pregnancy complications [5].
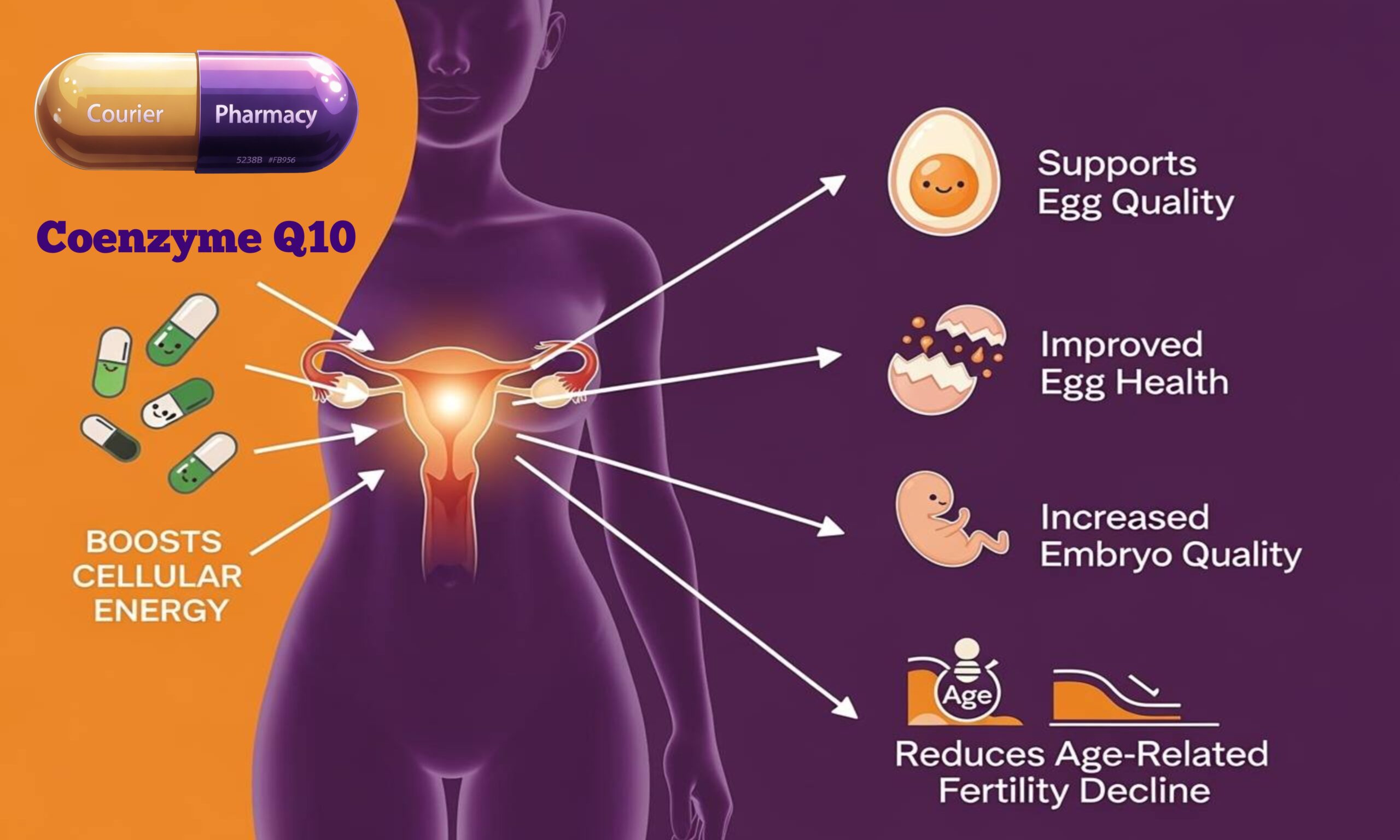
Coenzyme Q10 and female fertility
CoQ10 and ovarian reserve
Ovarian reserve is a term for the number and quality of eggs left in a woman’s ovaries. As women age, both decline—sometimes faster than expected. A randomised controlled trial found that women who took CoQ10 before IVF had better ovarian response, more eggs retrieved, and higher quality embryos compared to those who didn’t [6].
CoQ10 and egg quality
Eggs need a lot of energy to mature and be fertilised. CoQ10 supports this by boosting ATP production in the mitochondria. Studies show that CoQ10 supplementation can help improve both the number and quality of eggs, especially in older women or those with diminished ovarian reserve [7].
CoQ10 and pregnancy outcomes
Low CoQ10 is linked to higher rates of miscarriage and chromosomal abnormalities like Down syndrome. Adequate CoQ10 may help reduce these risks by supporting healthy cell division and embryo development [2].
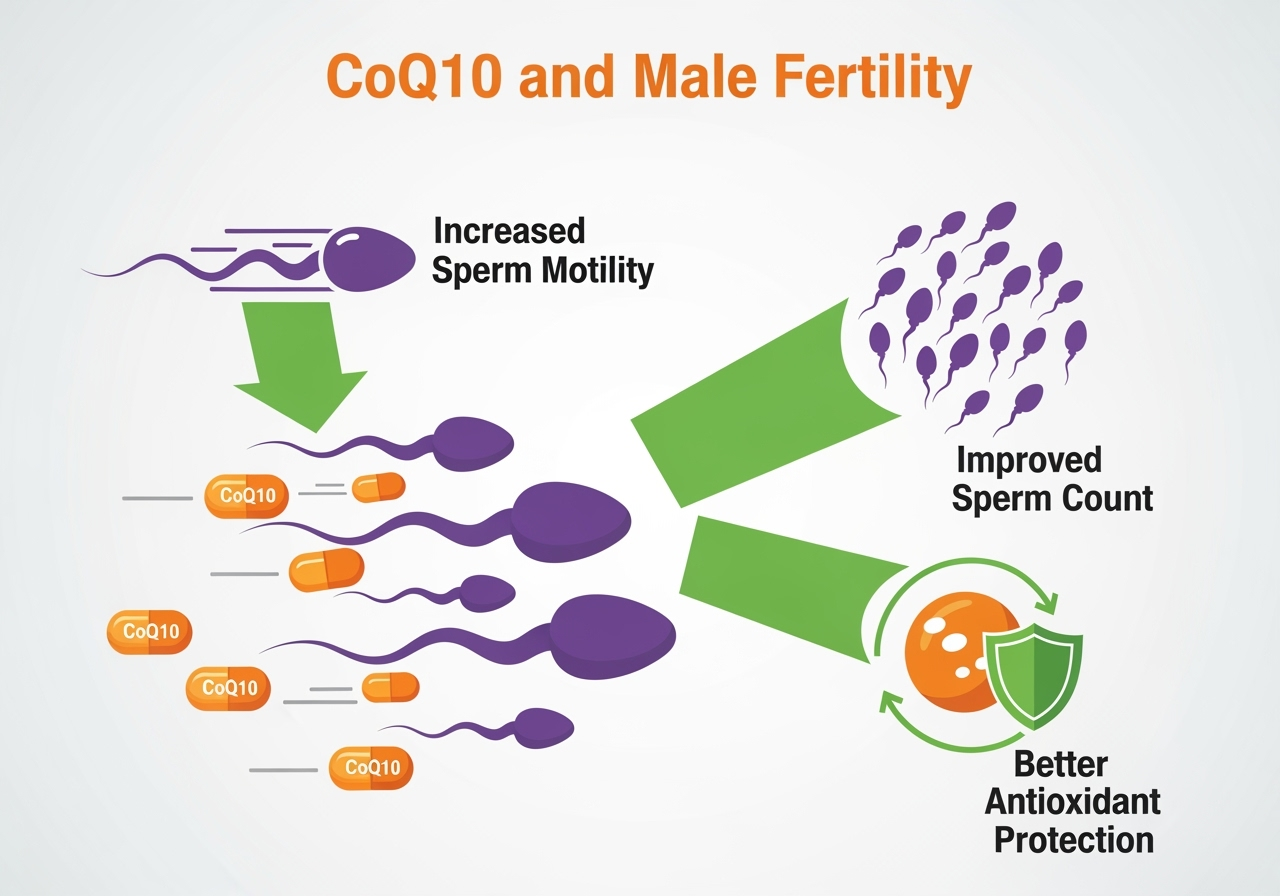
Coenzyme Q10 and male fertility
While this article focuses mainly on women, it’s worth noting that CoQ10 is also important for male fertility. Research shows that CoQ10 supplementation can improve sperm count, motility, and antioxidant status in men with low sperm quality [8].
What forms of coenzyme Q10 are available?
CoQ10 comes in two main forms: ubiquinone (the oxidised form) and ubiquinol (the reduced, more easily absorbed form). Both are fat-soluble, but ubiquinol is generally absorbed better. Most people can convert ubiquinone to ubiquinol in the body, but absorption can still vary [2].
How to improve absorption?
At Courier Pharmacy, you’ll find CoQ10 as a soluble oral patch, which dissolves in the mouth for direct absorption into the bloodstream—no need to go through the digestive system [1].
How much coenzyme Q10 should I take for fertility?
Most people get just 3–6mg of CoQ10 daily from food (think red meat, oily fish, legumes, broccoli, and spinach). For fertility support, research and expert opinion suggest a daily intake of 100–600mg. If you’re using a highly absorbable patch, lower doses may be enough [2].
How long should I take coenzyme Q10 for fertility?
Eggs take about 90 days to mature, so most fertility specialists recommend taking CoQ10 for at least three months before trying to conceive or starting fertility treatments [2].

Practical tips for boosting fertility with coenzyme Q10
- Start early: Begin taking CoQ10 at least three months before trying to conceive for best results.
- Choose the correct form: Consider a soluble oral patch for better absorption, especially if you have digestive issues.
- Pair with a healthy lifestyle: CoQ10 works best alongside a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking or excessive alcohol.
- Talk to your healthcare provider: Always check with your doctor or pharmacist before starting any new supplement, especially if you’re on medication or have health conditions.
- Be patient: Fertility improvements can take time—give your body at least a few months to respond.
FAQs
What is coenzyme Q10, and why is it important for fertility?
Coenzyme Q10 is a vitamin-like compound that helps your cells produce energy and acts as a powerful antioxidant. Both egg and sperm cells need lots of energy and protection from damage, so CoQ10 is crucial for fertility [1].
Does coenzyme Q10 improve egg quality?
Research suggests that CoQ10 supplementation can improve both the number and quality of eggs, especially in women with low ovarian reserve or those over 35 [6].
Can coenzyme Q10 help male fertility?
Yes! Studies show that CoQ10 can improve sperm count, motility, and antioxidant status in men with poor semen quality [2].
How much coenzyme Q10 should I take for fertility?
Most experts recommend 100–600mg per day, but always check with your healthcare provider for personalised advice [2].
Is it better to take ubiquinone or ubiquinol?
Both forms are effective, but ubiquinol is usually better absorbed. If you have trouble with absorption or digestive issues, a soluble oral patch may be a good option [2].
How long should I take coenzyme Q10 before trying to conceive?
Aim for at least three months, as eggs take about 90 days to mature. Consistency is key! [2].
Can I get enough coenzyme Q10 from food?
Most people only get a small amount from diet alone, so supplements are usually needed for fertility benefits [2].
Are there any side effects of coenzyme Q10?
CoQ10 is generally well tolerated, but some people may experience mild stomach upset or headaches. Always follow recommended doses and check with your doctor if unsure.
Can I take coenzyme Q10 with other fertility supplements?
Yes, CoQ10 can be taken alongside most other fertility supplements, but it’s always best to check with your healthcare provider first.
Where can I buy coenzyme Q10?
You can find CoQ10 supplements, including capsules and soluble oral patches, at courierpharmacy.co.uk. Our team is happy to help you choose the right option for your needs.
References
- [1] Medical Mojo (n.d.) What’s the role of CoQ10 in fertility? Available at: https://medicalmojo.co.uk/whats-the-role-of-coq10-in-fertility/ (Accessed: 11 August 2025).
- [2] Medical Mojo (n.d.) CoQ10 and fertility. Available at: https://medicalmojo.co.uk/coq10-and-fertility/ (Accessed: 11 August 2025).
- [3] Bentinger, M., Brismar, K. and Dallner, G., 2007. The antioxidant role of coenzyme Q. Mitochondrion, 7, pp.S41-S50.
- [4] Casagrande, D., Waib, P.H. and Júnior, A.A.J., 2018. Mechanisms of action and effects of the administration of Coenzyme Q10 on metabolic syndrome. Journal of Nutrition & Intermediary Metabolism, 13, pp.26-32.
- [5] Cogliati, S., Cabrera-Alarcón, J.L. y Enríquez, J.A., 2021. Regulation and functional role of the electron transport chain supercomplexes. Biochemical Society Transactions, 49(6), pp.2655-2668.
- [6] Xu, Y., Nisenblat, V., Lu, C., Li, R., Qiao, J., Zhen, X. and Wang, S., 2018. Pretreatment with coenzyme Q10 improves ovarian response and embryo quality in low-prognosis young women with decreased ovarian reserve: a randomised controlled trial. Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology, 16, pp.1-11.
- [7] Ben-Meir, A., Burstein, E., Borrego-Alvarez, A., et al. (2015). Coenzyme Q10 restores oocyte mitochondrial function and fertility during reproductive ageing. Aging cell, 14(5), 887–895.
- [8] Alahmar, A.T. (2019). The impact of two doses of coenzyme Q10 on semen parameters and antioxidant status in men with idiopathic oligoasthenoteratozoospermia. Clinical and experimental reproductive medicine, 46(3), 112–118.


